09-11-2024 - Linear Algebra - rank of a matrix [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
09-11-2024 - Linear Algebra - rank of a matrix [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_083)
rank of a matrix
The rank of a matrix, also called characteristic of the matrix, is a number that represents the maximum number of rows or columns of the matrix that you think of as vectors are linearly independent.
Equivalent facts
-In a square matrix the columns are linearly independent.
-In a square matrix the rows are linearly independent.
-the determinant of the matrix is different from zero.
Example of a rank
In the following example I express the rank of a matrix that is related to the linear independence of the column vectors.
So the rank of A is said to be the maximum number of linearly independent columns of a matrix A of dimension n x m.
This is reported by the following writing
rank(A)
Take the following matrix as an example
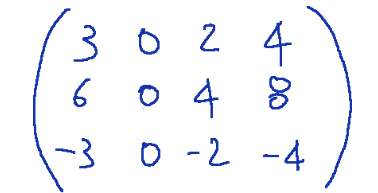
In this case all the column vectors are multiples of the first
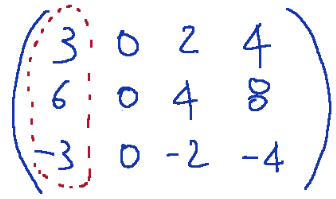
so they are linearly independent.
The first column vector is linearly independent.
Let's try to calculate the rank of a 2 x 2 square matrix with Kronecker's theorem.
Below is the square matrix taken into consideration.
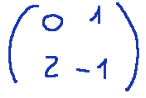
If we use Kronecker's Theorem to calculate the rank of a matrix we must verify the order of the non-zero minors of the matrix. In particular, an n x n matrix has rank r if and only if there exists at least one minor of order r different from zero, while all minors of order higher than r are zero.
The matrix we want to analyze is the following:
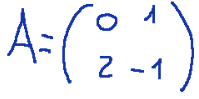
The steps for calculating the rank
first step - calculating the minors of order 1
Let's consider the individual elements of the matrix and if at least one is different from zero then the rank is at least 1.
The elements, in this case are 0, 1, 2, -1 and there are three elements different from zero, so we can already deduce that the rank of the matrix is at least one.
Second step - calculating the minor of order 2 (determinant of the matrix)
If the determinant of the matrix A is different from zero, then the rank is 2.
Here is the formula for calculating the determinant
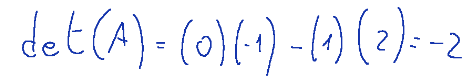
Since the determinant is different from zero we can reach the conclusion by stating that the rank of the matrix is 2
Result
The rank of the matrix A is 2
Conclusions
The rank of a matrix indicates the maximum number of linearly independent rows or columns in a matrix.
Question
Have you ever studied the rank of a matrix at school?

[ITALIAN]
09-11-2024 - Algebra lineare - rango di una matrice [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_083)
rango di una matrice
Il rango di una matrice, detto anche caratteristica della matrice, è un numero che rappresenta il massimo numero di righe o di colonne della matrice che pensate come vettori sono linearmente indipendenti.
Fatti equivalenti
-In una matrice quadrata le colonne sono linearmente indipendenti.
-In una matrice quadrata le righe sono linearmente indipendenti.
-il determinante della matrice è diverso da zero.
Esempio di un rango
Nel seguente esempio esprimo il rango di una matrice che è legato alla indipendenza lineare dei vettori colonna.
Quindi è detto rango di A il massimo numero di colonne linearmente indipendenti di una matrice A di dimensione n x m.
Questo si riporta tramite la seguente scrittura
rank(A)
Prendiamo come esempio la seguente matrice
In questo caso tutti i vettori colonna sono multipli del primo

quindi essi sono linearmente indipendenti.
Il primo vettore colonna è linearmente indipendente.
Proviamo a calcolare il rango di una matrice quadrata 2 x 2 con il teorema di Kronecker.
Qui di seguito la matrice quadrata presa in considerazione.
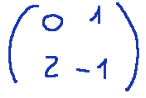
Se usiamo il Teorema di Kronecker per calcolare il rango di una matrice dobbiamo verificare l’ordine dei minori non nulli della matrice. In particolare, una matrice n x n ha rango r se e solo se esiste almeno un minore di ordine r diverso da zero, mentre tutti i minori di ordine superiore a r sono nulli.
La matrice che vogliamo analizzare è la seguente:
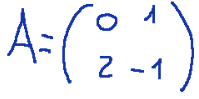
I passi per il calcolo del rango
primo passo - calcolo dei minori di ordine 1
Consideriamo i singoli elementi della matrice e se almeno uno è diverso da zero allora il rango è almeno 1.
Gli elementi, in questo caso sono 0, 1, 2, -1 e ci sono tre elementi diversi da zero, quindi possiamo già dedurre che il rango della matrice è almeno uno.
Secondo passo - calcolo del minore di ordine 2 (determinante della matrice)
Se il determinante della matrice A è diverso da zero, allora il rango è 2.
Qui di seguito la formula per il calcolo del determinante
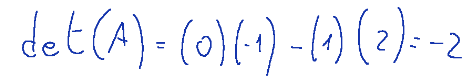
Poiché il determinante è diverso da zero possiamo arrivare alla conclusione affermando che il rango della matrice è 2
Risultato
Il rango della matrice A è 2
Conclusioni
Il rango di una matrice indica il numero massimo di righe o colonne linearmente indipendenti in una matrice.
Domanda
Avete mai studiato a scuola il rango di una matrice?
THE END
https://x.com/lee19389/status/1855220323030827062
#hive #posh
I’ve never studied the rank of a Matrix
It’s a difficult course, lol
Matrixes are an interesting mathematics topic and I like how you laid out the explanations and calculations. It's an interesting lesson, thanks for sharing.
!PIZZA
$PIZZA slices delivered:
@cryptoyzzy(5/5) tipped @stefano.massari
thehockeyfan-at tipped stefano.massari
!PIZZA
!LOL
!INDEED
lolztoken.com
The A-gull and B-gull weren't quite right.
Credit: reddit
@stefano.massari, I sent you an $LOLZ on behalf of cryptoyzzy
(5/10)
NEW: Join LOLZ's Daily Earn and Burn Contest and win $LOLZ
(5/10)
@stefano.massari! @cryptoyzzy Totally agrees with your content! so I just sent 1 IDD to your account on behalf of @cryptoyzzy.
One subject i hate more is math, i suck at it would prefer history to math anyday
History is a subject that I also like a lot. !INDEED
Well despite the fact they dont always tell us the truth its still a great way to look at the world from aback
(1/5)
@fredaig! @stefano.massari Totally agrees with your content! so I just sent 1 IDD to your account on behalf of @stefano.massari.