Linear Approximation - Introduction and Examples
In this video I introduce linear approximation and go through some useful examples detailing how to use it and also how accurate it can be.
Watch video on:
- 3Speak:
- Odysee: https://odysee.com/@mes:8/Linear-Approximation-Introduction-and-Examples:b
- BitChute: https://www.bitchute.com/video/Msj7tdzKqjYJ/
- Rumble:
- DTube: https://d.tube/#!/v/mes/nts8e33fxv7
- YouTube: https://youtu.be/bXEK8bkWTtM
Download video notes: https://1drv.ms/b/s!As32ynv0LoaIib9ZRLBrz8y8lHcccQ?e=DyTJdw
View Video Notes Below!
Download these notes: Link is in video description.
View these notes as an article: https://peakd.com/@mes
Subscribe via email: http://mes.fm/subscribe
Donate! :) https://mes.fm/donate
Buy MES merchandise! https://mes.fm/store
More links: https://linktr.ee/matheasy
Follow my research in real-time on my MES Links Telegram: https://t.me/meslinks
Subscribe to MES Truth: https://mes.fm/truthReuse of my videos:
- Feel free to make use of / re-upload / monetize my videos as long as you provide a link to the original video.
Fight back against censorship:
- Bookmark sites/channels/accounts and check periodically
- Remember to always archive website pages in case they get deleted/changed.
Recommended Books:
- "Where Did the Towers Go?" by Dr. Judy Wood: https://mes.fm/judywoodbook
Join my forums!
- Hive community: https://peakd.com/c/hive-128780
- Reddit: https://reddit.com/r/AMAZINGMathStuff
- Discord: https://mes.fm/chatroom
Follow along my epic video series:
- #MESScience: https://mes.fm/science-playlist
- #MESExperiments: https://peakd.com/mesexperiments/@mes/list
- #AntiGravity: https://peakd.com/antigravity/@mes/series
-- See Part 6 for my Self Appointed PhD and #MESDuality breakthrough concept!- #FreeEnergy: https://mes.fm/freeenergy-playlist
- #PG (YouTube-deleted series): https://peakd.com/pg/@mes/videos
NOTE #1: If you don't have time to watch this whole video:
- Skip to the end for Summary and Conclusions (if available)
- Play this video at a faster speed.
-- TOP SECRET LIFE HACK: Your brain gets used to faster speed!
-- MES tutorial: https://peakd.com/video/@mes/play-videos-at-faster-or-slower-speeds-on-any-website- Download and read video notes.
- Read notes on the Hive blockchain #Hive
- Watch the video in parts.
-- Timestamps of all parts are in the description.Browser extension recommendations:
- Increase video speed: https://mes.fm/videospeed-extension
- Increase video audio: https://mes.fm/volume-extension
- Text to speech: https://mes.fm/speech-extension
--Android app: https://mes.fm/speech-android
Linear Approximation
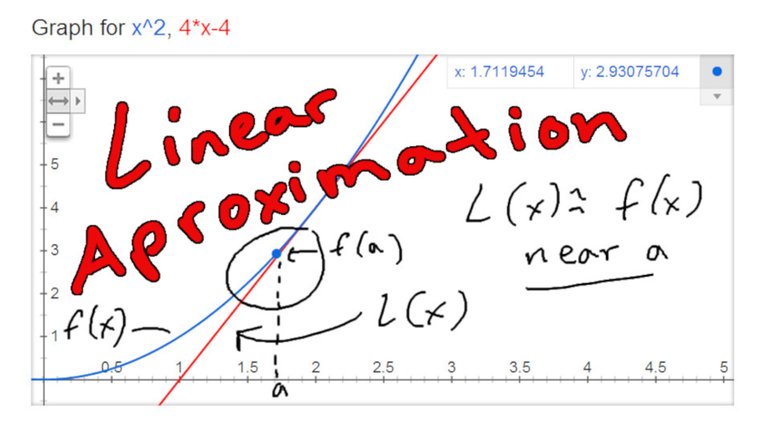
An Introduction
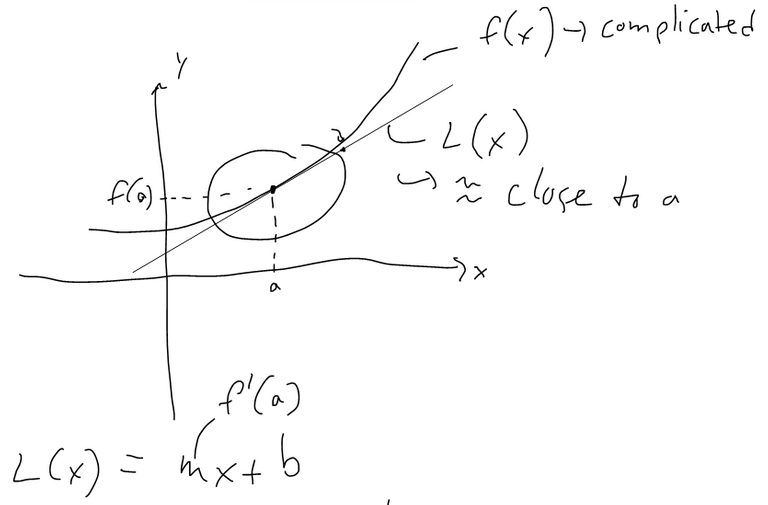
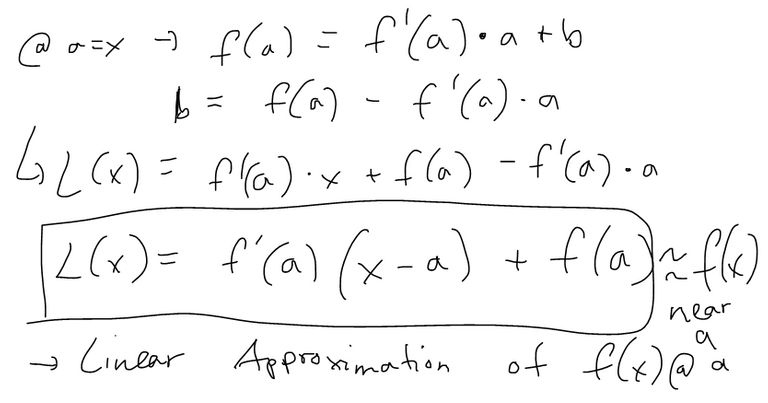
Example 1
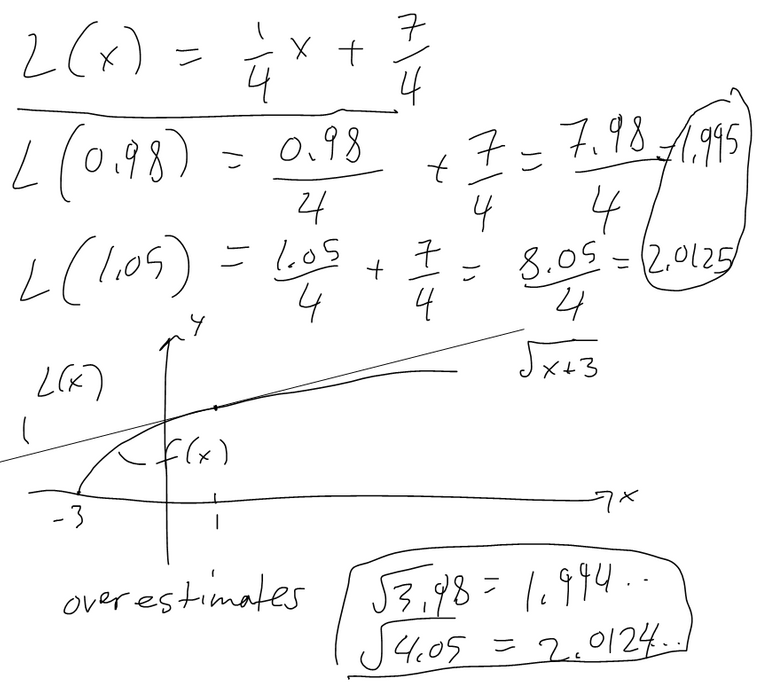
Suppose that after you stuff a turkey its temperature is 50 degrees F and you then put it in a 325 degrees F oven. After an hour the meat thermometer indicates that the temperature of the turkey is 93 degrees F and after two hours it indicates 129 degrees F. Predict the temperature of the turkey after 3 hours.
Solution:
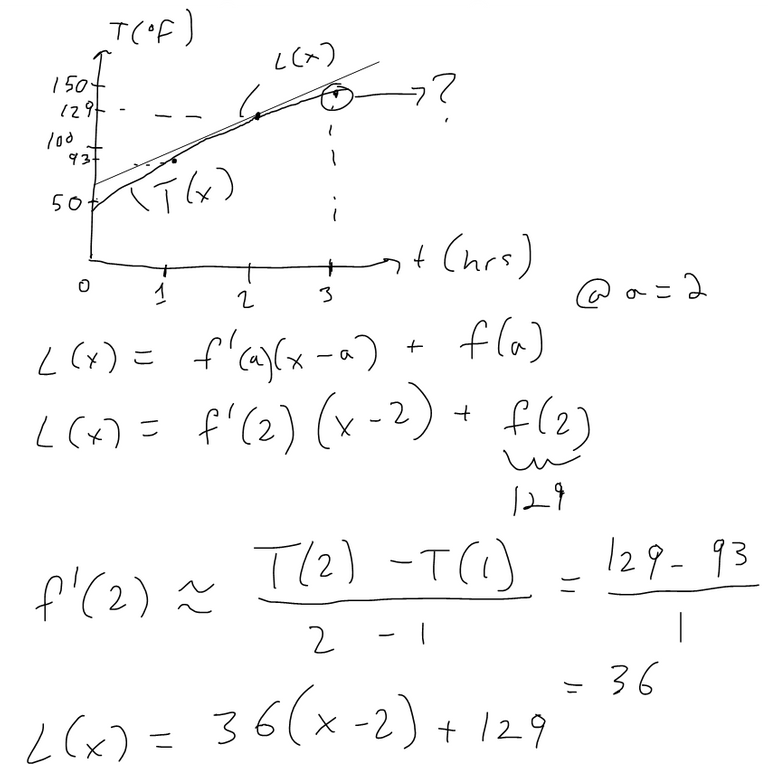
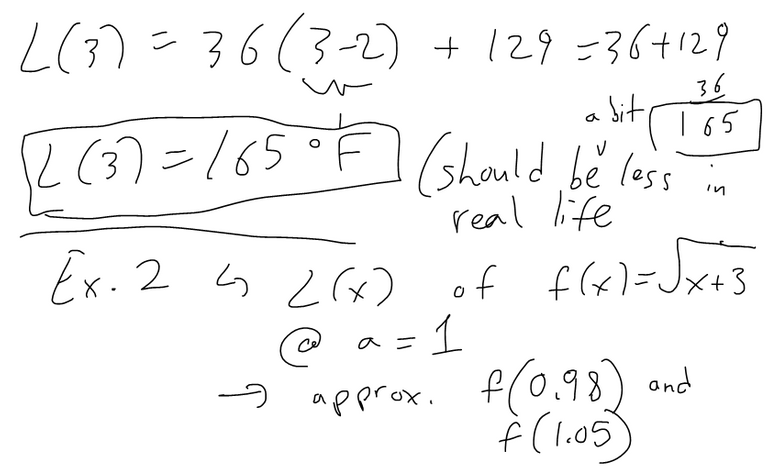
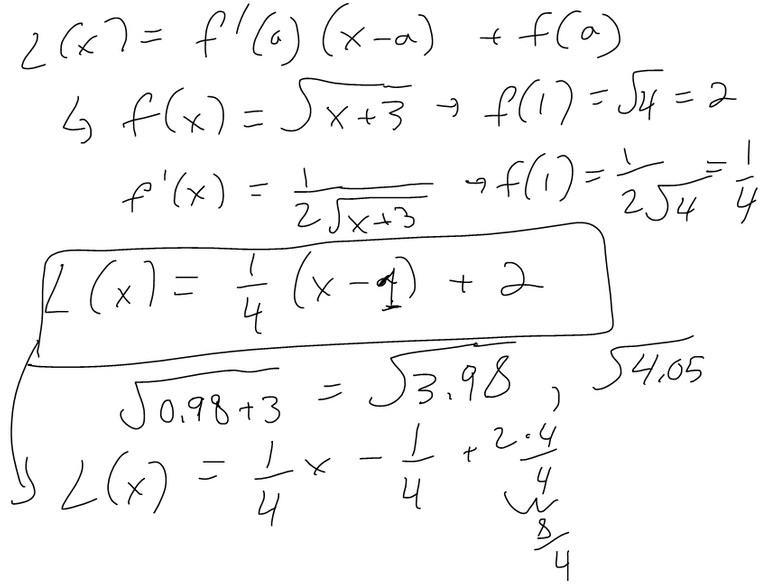
Cool, could you do a video on something I had to think about in order to reduce colors in an image, look at the following saying:
Then my question is: given those concepts (my code here, https://dev.to/vipert/quantimat-reduce-of-20x-some-colors-within-88ms-down-to-2000-2pho) what are called such a reduction passing through binary values in mathematics?
Interesting. I had not worked on such a problem before. But searching online, I believe this "K-Means method" may be what you are looking for: https://muthu.co/reduce-the-number-of-colors-of-an-image-using-k-means-clustering/
Yeah it is similar it works with defining kind of clusters too yet it happens to add random variables and add similar entry around those random points, rather with binary reduction it's fast and deterministic but you have a lot of blending operation to do per clusters...
https://twitter.com/442160704/status/1628837556409470977
The rewards earned on this comment will go directly to the people( @mes ) sharing the post on Twitter as long as they are registered with @poshtoken. Sign up at https://hiveposh.com.
https://reddit.com/r/AMAZINGMathStuff/comments/11a660p/linear_approximation_introduction_and_examples/
The rewards earned on this comment will go directly to the people sharing the post on Reddit as long as they are registered with @poshtoken. Sign up at https://hiveposh.com.