31-03-2024 - Physics - Fundamentals of thermodynamics (9/13) [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
31-03-2024 - Physics - Fundamentals of thermodynamics (9/13) [EN]-[IT]
Conduction and radiation
Thermal conduction means that heat transmission occurs in a solid, liquid or gaseous medium
Radiation is the transfer of energy (or heat in the case of thermal radiation) between two bodies by means of electromagnetic waves.
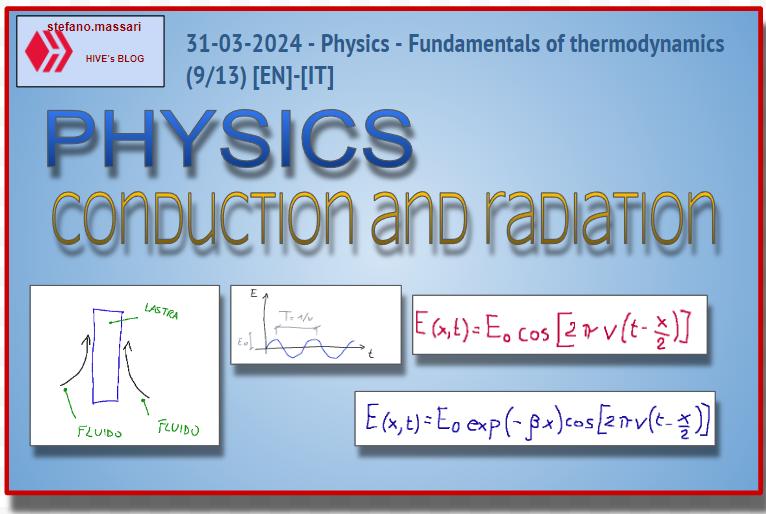
Conduction in non-stationary regime
Example
The most classic example is that of a plate touched by a fluid
Biot's number
The Biot number is the ratio of the conductive resistivity inside the plate to the convective resistivity outside the plate.
Thermal radiation
What is it?
Thermal radiation is one of the mechanisms for transferring thermal energy. It is always present in the phenomena of thermal exchange between bodies, however, in some cases it is negligible compared to the other two mechanisms, conduction and convection.
Characteristics
Peculiar characteristics of thermal radiation are only the possibility of propagation in the absence of an intervening medium, unlike conduction and convection, and the functional dependence on temperature.
Thermal radiation is radiation emitted due to temperature.
Emission without dissipation
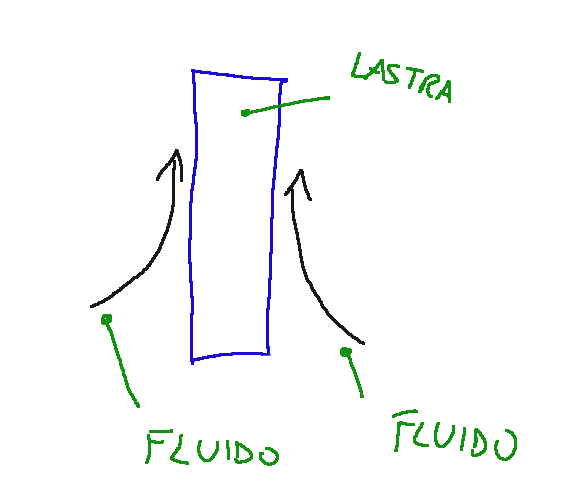
Diagram
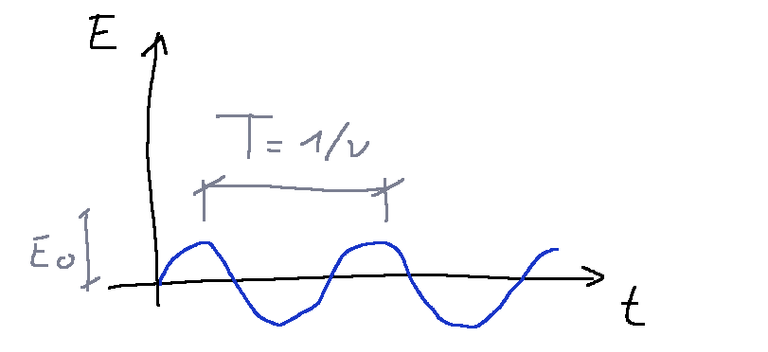
Law
The law by which the amplitude of the waves emitted with dissipation by an oscillating wall varies is the following (case without dissipation).
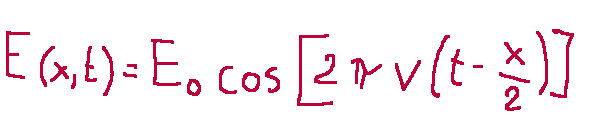
Where:
E0 = maximum extension of oscillation
v = 1/T = frequency of the oscillation, i.e. number of cycles in the unit of time;
Emission with dissipation
Law
Below is the law by which the amplitude of the waves emitted with dissipation by an oscillating wall varies (case with dissipation).
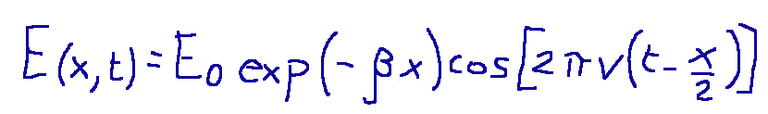
Where:
β = attenuation coefficient
Energy emitted
Hemispherical emissive power
The total hemispheric emissive power represents the radiant thermal energy emitted by a surface, per unit of time and area, in all directions and on all wavelengths.
Simplification
In a more simplified way we can say that a surface of a certain material can emit energy in the form of electromagnetic waves in all directions, at different wavelengths.
Conclusions
Radiation is one of the ways of transferring thermal energy and is always present in the phenomena of thermal exchanges between bodies.
Request
Have you ever studied radiation at school?

31-03-2024 - Fisica - Fondamenti di termodinamica (9/13) [EN]-[IT]
Conduzione e irraggiamento
Per conduzione termica si intende che la trasmissione di calore avviene in un mezzo solido, liquido o aeriforme
L'irraggiamento è il trasferimento di energia (oppure calore nel caso di irraggiamento termico) tra due corpi per mezzo di onde elettromagnetiche.
La conduzione in regime non stazionario
Esempio
L'esempio più classico è quello di una lastra lambita da un fluido

Il numero di Biot
Il numero di Biot è il rapporto fra la resistività conduttiva all'interno della lastra e la resistività convettiva all'esterno della lastra.
Irraggiamento termico
Che cosa è?
L'irraggiamento termico è uno dei meccanismi di trasferimento dell'energia termica. Esso è sempre presente nei fenomeni di scambi termici tra corpi, però, in alcuni casi risulta trascurabile rispetto agli altri due meccanismi, la conduzione e la convezione.
Caratteristiche
Caratteristiche peculiari dell’irraggiamento termico solo la possibilità di propagazione in assenza di mezzo interposto, a differenza della conduzione e della convezione, e la dipendenza funzionale dalla temperatura.
La radiazione termica è quella radiazione emessa a causa della temperatura.
Emissione senza dissipazione
Diagramma

Legge
La legge con cui varia l'ampiezza delle onde emesse con dissipazione da una parete che oscilla è la seguente (caso senza dissipazione).
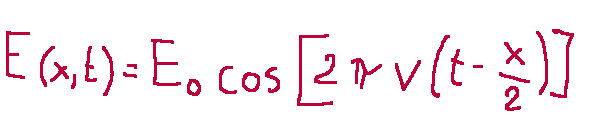
Dove:
E0 = massima estensione dell’oscillazione
v = 1/T = frequenza dell’oscillazione, ovvero numero di cicli nell’unità di tempo;
Emissione con dissipazione
Legge
Qui di seguito la legge con cui varia l'ampiezza delle onde emesse con dissipazione da una parete che oscilla (caso con dissipazione).
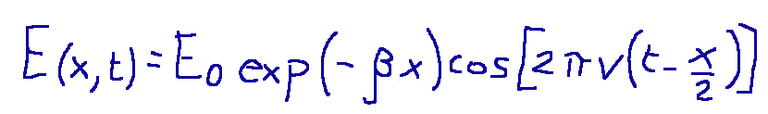
Dove:
β = coefficiente di attenuazione
Energia emessa
Potere emissivo emisferico
Il potere emissivo emisferico totale rappresenta l'energia termica raggiante emessa da una superficie, per unità di tempo e di area, in tutte le direzioni e su tutte le lunghezze d'onda.
Semplificazione
In maniera più semplificata possiamo dire che una superficie di un certo materiale, può emettere energia sotto forma di onde elettromagnetiche in tutte le direzioni, a diverse lunghezze d’onda.
Conclusioni
L'irraggiamento è uno dei modi di trasferimento dell'energia termica ed sempre presente nei fenomeni di scambi termici tra corpi.
Domanda
Avete mai studiato l'irraggiamento a scuola?
THE END
No! Radiation wasn’t taught at schools here! We ought to have more scientific knowledge!
This course seem hard to me though
Thanks for teaching
I so much love the dynamics of the radiation been passed across
Wow you really put in a great work to make sure that this lecture is well explanatory
Non ho visto questo argomento