26-03-2025 - Chemistry Basics - Spontaneity of Processes [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH

26-03-2025 - Chemistry Basics - Spontaneity of Processes [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_67)
image created with artificial intelligence, Microsoft Copilot software

Spontaneity of processes
Description
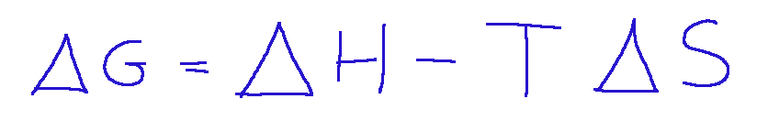
When we talk about spontaneity of processes in chemistry, it means that we are trying to understand the tendency of a reaction to occur without the need for external intervention.
Conceptually, the spontaneity of processes means a particular process that occurs without the addition of energy from the outside. When we enter into this particular topic, Gibbs nations come to our aid. In fact, it is said that spontaneity is determined by the Gibbs free energy. It is measured by ΔG.
When this term is less than zero, we know that the process occurs spontaneously. this was the first thing to clarify, while the second thing we need to take into account is entropy (ΔS). Entropy is in fact another factor that influences spontaneity and as we have seen in some previous posts it measures the degree of disorder. the rule that surrounds the spontaneity of processes in chemistry is that an increase in entropy tends to favor spontaneity.
We can summarize all this in the following sentence:
Both in thermodynamics and in chemistry, the spontaneity of processes indicates a spontaneous process that occurs naturally and, once started, continues without the need for additional energy from the outside. An example could be ice that turns into water only with the change in temperature.
Gibbs free energy
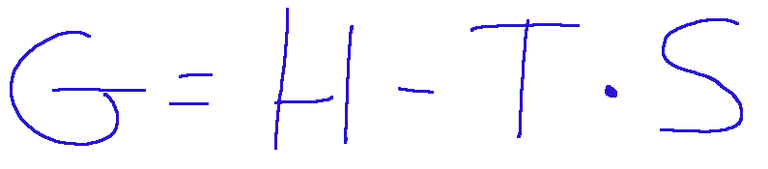
Gibbs free energy (G) is a function that allows us to determine whether a chemical process is spontaneous. What does it mean that a physical process is spontaneous? A chemical process is spontaneous if it will occur without the need for additional energy from the outside. Gibbs free energy is therefore a fundamental quantity, especially in thermodynamics, and is used to predict the spontaneity of chemical reactions at constant temperature and pressure.
Gibbs free energy is defined as:
G = H - T * S
Where:
G = Gibbs free energy
H = enthalpy of the system (total energy of the system)
T = absolute temperature (in Kelvin)
S = entropy of the system (measure of disorder or randomness of the system)
fundamental criterion of spontaneity of chemical-physical processes
The fundamental criterion for determining the spontaneity of chemical-physical processes is based on the variation of Gibbs free energy (ΔG).
In the mathematical relationship of this criterion, the effect of enthalpy and entropy in relation to temperature is combined. We do this to predict the spontaneity of a reaction at constant temperature and pressure. The formula that expresses this criterion is the following:
ΔG = ΔH - T * ΔS
Where:
ΔG = change in Gibbs free energy
ΔH = change in enthalpy which represents the heat exchanged during the reaction at constant pressure.
T = temperature
ΔS = change in entropy which measures the change in disorder or randomness of the system.
Conditions of Spontaneity
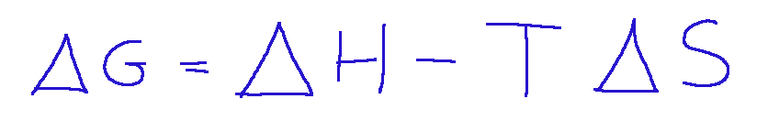
If ΔG < 0, the process is spontaneous.
If ΔG > 0, the process is not spontaneous.
If ΔG = 0, the system is in equilibrium.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we can say that a chemical process is spontaneous if it reduces the free energy of the system and this often occurs through an increase in entropy. A spontaneous process is one that occurs naturally, that is, without the addition of energy from the outside.
Question
A practical example of the application of Gibbs free energy is the dissolution of salt in water. Salt dissolves spontaneously at room temperature. We have always seen it with our own eyes, but have you ever thought that the dissolution of salt is simply a spontaneous process? That is, it occurs without the need for additional energy from the outside?

[ITALIAN]

26-03-2025 - Basi di chimica - Spontaneità dei processi [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_67)
immagine creata con l'intelligenza artificiale, software Microsoft Copilot

Spontaneità dei processi
Descrizione
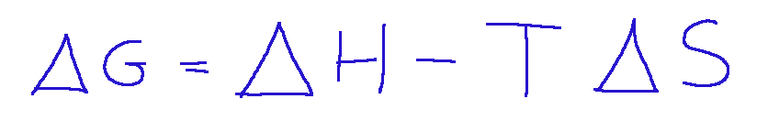
Quando parliamo di spontaneità dei processi in chimica, vuol dire che stiamo cercando di capire la tendenza di una reazione a verificarsi senza bisogno di intervento esterno.
Concettualmente, la spontaneità dei processi, significa un particolare processo che avviene senza l’aggiunta di energia dall’esterno.quando entriamo in questo particolare argomento ci vengono in aiuto le nazioni di Gibbs. Infatti, si dice che la spontaneità è determinata dall’energia libera di Gibbs. Essa si misura con ΔG.
Quando questo termine è minore di zero, sappiamo che il processo avviene spontaneamente. questa era la prima cosa da chiarire, mentre la seconda cosa di cui dobbiamo tener conto è l’entropia (ΔS). L’entropia infatti è un altro fattore che influisce sulla spontaneità e come abbiamo visto in alcuni post in precedenza misura il grado di disordine.la regola che c’è attorno alla spontaneità dei processi in chimica è quella che un aumento dell’entropia tende a favorire la spontaneità.
Possiamo riassumere tutto questo nella seguente frase:
Sia termodinamica che in chimica, la spontaneità dei processi indica un processo spontaneo che avviene naturalmente e, una volta iniziato, prosegue senza necessità di energia aggiuntiva dall'esterno. Un esempio può essere il ghiaccio che si trasforma in acqua solo con il cambio di temperatura.
Energia libera di Gibbs
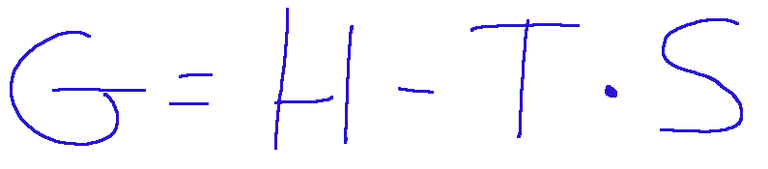
L’energia libera di Gibbs (G) è una funzione che ci permette di determinare se un processo chimico è spontaneo. Cosa significa che un processo fisico è spontaneo? Un processo chimico è spontaneo se avverrà senza bisogno di energia aggiuntiva dall’esterno. L’energia libera di Gibbs è quindi una grandezza fondamentale, soprattutto in termodinamica, ed è utilizzata per predire la spontaneità delle reazioni chimiche a temperatura e pressione costanti.
L’energia libera di Gibbs è definita come:
G = H - T * S
Dove:
G = energia libera di Gibbs
H = entalpia del sistema (energia totale del sistema)
T = temperatura assoluta (in Kelvin)
S = l'entropia del sistema (misura del disordine o della casualità del sistema)
criterio fondamentale sulla spontaneità dei processi chimico-fisici
Il criterio fondamentale per determinare la spontaneità dei processi chimico-fisici si basa sulla variazione dell’energia libera di Gibbs (ΔG).
Nella relazione matematica di questo criterio si combina l’effetto dell’entalpia e dell’entropia in relazione alla temperatura. Facciamo questo per prevedere la spontaneità di una reazione a temperatura e pressione costanti. La formula che esprime questo criterio è la seguente:
ΔG = ΔH - T * ΔS
Dove:
ΔG = variazione dell'energia libera di Gibbs
ΔH = variazione di entalpia che rappresenta il calore scambiato durante la reazione a pressione costante.
T = temperatura
ΔS = variazione di entropia che misura il cambiamento nel disordine o nella casualità del sistema.
Condizioni di spontaneità
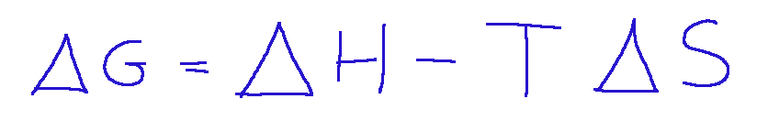
Se ΔG < 0, il processo è spontaneo.
Se ΔG > 0, il processo non è spontaneo.
Se ΔG = 0, il sistema è in equilibrio.
Conclusioni
In conclusione, possiamo dire che un processo chimico è spontaneo se riduce l’energia libera del sistema e questo spesso avviene attraverso l’aumento dell’entropia. Un processo spontaneo è quello che avviene naturalmente, cioè senza l'aggiunta di energia dall'esterno.
Domanda
Un esempio pratico dell'applicazione dell'energia libera di Gibbs è la dissoluzione del sale in acqua. Il sale si scioglie spontaneamente a temperatura ambiente. L'abbiamo sempre visto con i nostri occhi, ma avete mai pensato che la dissoluzione del sale è semplicemente un processo spontaneo? Cioè avviene senza la necessità di energia aggiuntiva dall'esterno?
THE END
I must say I really admire your teaching skills. It is really top notch for me
Thank you for your kind words.
I believe that knowing whether a chemical reaction can be spontaneous or not is important, for this reason I wanted to write an article specifically about the conditions of spontaneity of a chemical reaction. This spontaneity of a reaction is often evaluated using the Gibbs free energy.
I’ll try out the salt and water practical to prove what you’re saying
Thanks for stopping by. In chemistry, the spontaneity of a process is determined by the change in Gibbs free energy (ΔG). A process is spontaneous if ΔG is negative, indicating that the system can evolve without the need for external energy. This is where salt comes into play. The behavior of salts in aqueous solution is closely linked to these thermodynamic concepts. When a salt dissolves in water, the solid crystal lattice disintegrates. without the need for external energy.
What if we look at the other way around, cant salt dissolve in water because of the water polar molecules present ??
Thanks for leaving a comment and asking this question. I think you are right too. I will try to answer, but I am just someone who has studied certain concepts and I am not an expert. From what I know, it is precisely thanks to the polar nature of water that many salts can dissolve in it. Water is in fact a polar solvent. Water molecules have an asymmetric distribution of charges. Oxygen is slightly negative, hydrogens are slightly positive. This makes them capable of interacting with the ions present in salts.
hmmm ok thats another way to look at it then
Spontaneity means a process occurs naturally
without extra energy. If ΔG < 0, it's spontaneous! 🔬
I already asked you if you work in the chemical sector or are you a chemistry enthusiast? You know a lot of things. We can simplify by saying that the Spontaneity conditions are three:
1-If ΔG < 0, the process is spontaneous.
2-If ΔG > 0, the process is not spontaneous.
3-If ΔG = 0, the system is in equilibrium.
I believe that the spontaneity conditions in chemistry are a very important thing because they are the ones that determine whether a chemical reaction occurs spontaneously without the intervention of external factors.
@stefano.massari, I paid out 0.134 HIVE and 0.031 HBD to reward 4 comments in this discussion thread.