26-02-2025 - Chemistry Basics - The Periodic Table [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
26-02-2025 - Chemistry Basics - The Periodic Table [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction on the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_92)
The Periodic Table
Below is an image of the periodic table.
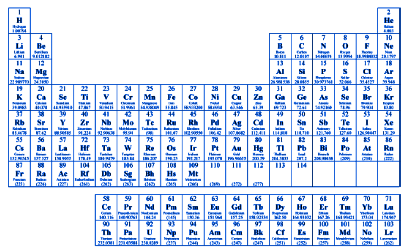
The periodic table of elements is a table in which the chemical elements are ordered based on their atomic number Z and the number of electrons present in the atomic orbitals.
This table was created by the Russian chemist Dmitrij Ivanovič Mendeleev, born in 1834 and died in 1907. He was also awarded several Russian honors and a French one.
How the periodic table is formed
With the aufbau (filling) mechanism, applied to the atoms ordered according to increasing z and going to the line (period) after having reached the ns2 np6 configuration (typical of the noble gas), or after having reached the octet (8 e- on the last level: particularly stable spherical system), the periodic repetition of the external electronic structures along the group is highlighted.
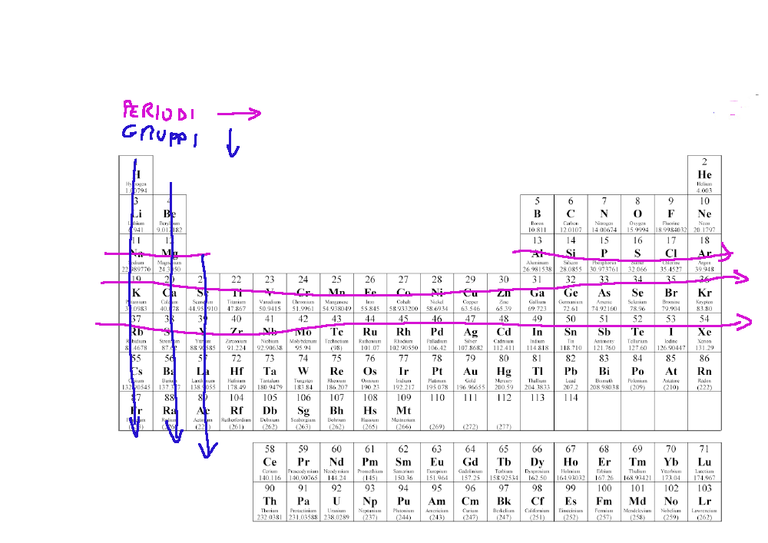
In the table, the periods are the horizontal rows of the table, while the groups are the vertical columns of the table.
The horizontal rows show the trend of the electron energy and other periodic properties.
The vertical columns instead show the elements with similar chemical properties.
NOTE: Chemical elements that belong to the third period have available D orbitals. These allow more than 8 electrons to be accommodated in the valence shell, thus expanding the octet.
NOTE 2: If we take carbon, fluorine and nitrogen we note that they belong to the second period and do not have d orbitals. These cannot expand the octet.
electronegativity
Electronegativity is a property of atoms that indicates the ability to attract shared electrons in a chemical bond.
Electronegativity consists in the attraction of electrons, which influences polarity.
In the periodic table, electronegativity increases from left to right along a period and decreases going down a group.
NOTE: Among Al, Si, S and P, sulfur (S) has the highest electronegativity value. All the proposed elements belong to the third period of the periodic table. Electronegativity increases from left to right along the same period.
ionization energy
This is a very important concept in chemistry. Ionization energy is the minimum energy needed to remove an electron from an atom or an isolated molecule in the gaseous phase, transforming it into a positive ion.
Basically, it is the amount of energy required to remove the outermost electron.
This energy is expressed in two units:
kJ/mol = kilojoule per mole
eV = in electronvolts
The first ionization energy of an atom
This energy is exactly the minimum energy needed to remove the outermost electron from an isolated neutral atom in the gaseous phase, transforming it into a positive ion. We can say that it is the amount of energy needed to tear the first valence electron from an atom.
Valence electrons are the electrons present in the outermost orbital of an atom.
We can also say this:
The first ionization energy of an atom is the minimum energy required to remove the outermost electron from an isolated atom to an infinite distance
NOTE: The element with the lowest first ionization energy is Cesium (Cs, alkali metal, located at the bottom of group 1 of the periodic table)
From left to right
Moving from left to right along the Periodic Table, the atomic radius tends to decrease.
Periodic properties of the elements
The chemical and physical characteristics that show a regular trend along the rows and columns of the periodic table are called periodic properties of the elements.
These properties vary according to the atomic number and electronic configuration of the atoms.
Reading the periodic table in particular we have that:
-The atomic radius tends to decrease from left to right and increases going down the column
-The ionization energy tends to increase from left to right along a period and decreases going down a group.
-Electronegativity (the ability of an atom to attract shared electrons in a chemical bond) increases along a period and decreases along a group.
Conclusions
The periodic table in chemistry is of fundamental importance because it organizes the elements by arranging them according to their atomic number and allows us to understand how an element can react in a given situation.
Question
Do you remember having already seen the periodic table of the elements? Did you remember that it was created by the Russian chemist Mendeleev?

[ITALIAN]
26-02-2025 - Basi di chimica - La tavola periodica [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_92)
La tavola periodica
Qui di seguito un immagine della tavola periodica.

La tavola periodica degli elementi è una tabella in cui sono ordinati gli elementi chimici sulla base del loro numero atomico Z e del numero di elettroni presenti negli orbitali atomici.
Questa tavola fu ideata dal chimico russo Dmitrij Ivanovič Mendeleev, nato nel 1834 e morto nel 1907. Egli fu insignito anche di diverse onorificenze russe e anche di una francese.
Come è formata la tavola periodica
Con il meccanismo dell’aufbau (riempimento), applicato agli atomi ordinati secondo z crescente e andando a capo (periodo) dopo aver raggiunto la configurazione ns2 np6 (propria del gas nobile), ovvero dopo aver raggiunto l’ottetto (8 e- sull’ultimo livello: sistema sferico particolarmente stabile), si evidenzia il ripetersi periodico delle strutture elettroniche esterne lungo il gruppo.
Nella tavola i periodi sono le righe orizzontali della tavola, mentre i gruppi le colonne verticali della tavola.
Le righe orizzontali mostrano l'andamento dell'energia degli elettroni e altre proprietà periodiche.
Le colonne verticali invece mostrano gli elementi con proprietà chimiche simili.

NOTA: Gli elementi chimici che appartengono al terzo periodo possiedono orbitali D disponibili. Questi consentono di ospitare più di 8 elettroni nel guscio di valenza, espandendo così l'ottetto.
NOTA 2: Se prendiamo il carbonio, il fluoro e l'azoto notiamo che appartengono al secondo periodo non dispongono di orbitali d. Questi non possono espandere l'ottetto.
elettronegatività
L'elettronegatività è una proprietà degli atomi che indica la capacità di attirare a sé gli elettroni condivisi in un legame chimico.
L'elettronegatività consiste nell'attrazione degli elettroni, influenza sulla polarità.
Nella tavola periodica l'elettronegatività aumenta da sinistra verso destra lungo un periodo e diminuisce scendendo lungo un gruppo.
NOTA: tra Al, Si, S e P, lo zolfo (S) possiede il valore più elevato di elettronegatività. Tutti gli elementi proposti appartengono al terzo periodo della tavola periodica. L'elettronegatività aumenta da sinistra verso destra lungo lo stesso periodo.
energia di ionizzazione
Questo è un concetto molto importante in chimica. L'energia di ionizzazione è l'energia minima necessaria per rimuovere un elettrone da un atomo o da una molecola isolata in fase gassosa, trasformandolo in uno ione positivo
Sostanzialmente è la quantità di energia richiesta per togliere l'elettrone più esterno.
Questa energia viene espressa in due unità di misura:
kJ/mol = kilojoule per mole
eV = in elettronvolt
L’energia di prima ionizzazione di un atomo
Questa energia è esattamente l'energia minima necessaria per rimuovere l'elettrone più esterno da un atomo neutro isolato in fase gassosa, trasformandolo in uno ione positivo. Possiamo dire che è la quantità di energia che serve per strappare il primo elettrone di valenza da un atomo.
Gli elettroni di valenza sono gli elettroni presenti nell'orbitale più esterno di un atomo.
Possiamo dire anche così:
L’energia di prima ionizzazione di un atomo è l’energia minima richiesta per allontanare a distanza infinita l’elettrone più esterno da un atomo isolato
NOTA: L’elemento con minore energia di prima ionizzazione è il Cesio (Cs, metallo alcalino, situato in fondo al gruppo 1 della tavola periodica)
Da sinistra verso destra
Spostandosi da sinistra verso destra lungo la Tavola Periodica il raggio atomico tende a diminuire.
Proprietà periodiche degli elementi
Le caratteristiche chimiche e fisiche che mostrano un andamento regolare lungo le righe e le colonne della tavola periodica vengono chiamate proprietà periodiche degli elementi.
Queste proprietà variano in funzione del numero atomico e della configurazione elettronica degli atomi.
Leggendo la tavola periodica in particolare abbiamo che:
-Il raggio atomico tende a diminuire da sinistra verso destra ed aumenta scendendo dalla colonna
-L'energia di ionizzazione tende ad aumentare da sinistra verso destra lungo un periodo e diminuisce scendendo lungo un gruppo.
-L'elettronegatività (la capacità di un atomo di attrarre a sé gli elettroni condivisi in un legame chimico) aumenta lungo un periodo e diminuisce lungo un gruppo.
Conclusioni
La tavola periodica in chimica è di fondamentale importanza perché organizza gli elementi disponendoli in base al numero atomico e permette di capire come un elemento potrà reagire in una determinata situazione.
Domanda
Vi ricordate di aver già visto la tavola periodica degli elementi? Ricordavate che fu ideata dal chimico russo Mendeleev?
THE END
I’m never someone who’s familiar with tables just as this isn’t easy for me too😅
I could even write a book about the periodic table, maybe I could make some other posts to understand it better
I remember been thought about this topic in chemistry. One of my favourite topic in chemistry then
Thanks for leaving a message. I think I could do 5 articles on HIVE on the periodic table. There would really be a lot to tell !WINE
!discovery 30
@tipu curate
Upvoted 👌 (Mana: 9/49) Liquid rewards.
This post was shared and voted inside the discord by the curators team of discovery-it
Join our Community and follow our Curation Trail
Discovery-it is also a Witness, vote for us here
Delegate to us for passive income. Check our 80% fee-back Program