20-03-2025 - Chemistry Basics - Gaseous State [EN]-[IT]

~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
20-03-2025 - Chemistry Basics - Gaseous State [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction about the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_75)
Gaseous State

Image generated with AI, software used Microsoft Copilot
Definition
The fundamental states of matter are 4:
-Solid
-Liquid
-Gaseous
-Plasma
So the gaseous state is one of the four fundamental states of matter, a state in which the molecules of a substance are separated by very large distances compared to the size of the molecules themselves. This condition allows gases to expand to fill the volume of the container in which they are located and to have a very low density compared to solids and liquids.
Characteristics
The main characteristics attributed to the gaseous state are listed below.
-Expansion
-Compressibility
-Low density
-Miscibility
where:
Miscibility = tendency of gases to mix completely with each other forming homogeneous mixtures.
Pressure
Pressure is one of the fundamental properties that characterize the gaseous state.
The pressure P is the force that a body exerts on a surface of unit area in a direction normal to the surface itself. In the International System (SI), pressure is measured in Pascal (Pa) or in bar.
However, other units of measurement are used throughout the world to measure pressure.
-atmospheres (atm);
-millimeters of mercury column (mm Hg);
-torricelli (torr) in honor of the physicist Evangelista Torricelli;
-meters of water column (m H2O);
-psi
Below is a line in which the various units of measurement and the relationship between them are expressed.
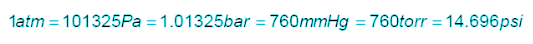
Boyle's Law
One of the main laws involving pressure and gases is Boyle's Law.
Boyle's Law describes the relationship between the pressure (P) and the volume (V) of a gas at constant temperature.
P x V = constant
Gay-Lussac's Law
Another important law in the study of the gaseous state is Gay-Lussac's Law.
Gay-Lussac's law describes the relationship between the pressure (P) and the temperature (T) of a gas at constant volume. It states that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
P / T = constant
Note: P and T are intensive quantities: they do not depend on the extension of the system but only on the point at which they are evaluated and on the time instant.
Temperature
When we are in the field of the study of gases we can say that temperature is one of the key variables that influence the behavior of gases.
Relationship between gas and temperature
When the temperature of a gas increases, the gas molecules acquire more kinetic energy and begin to move faster. This condition creates an expansion of the gas if the volume is variable, or an increase in pressure if the volume is constant.
In the SI it is measured in kelvin (K), which is an absolute unit of measurement, in the sense that 0 K is the absolute zero of the temperature: it is not possible to go below this value.
Charles' Law
In this case we can cite Charles' Law, which states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature at constant pressure. So the relationship is the following
V / T = constant
Equation of state of gases
Through a rudimentary experiment with a piston and a container we can observe the following.
Given T and varying P we observe that the volume V varies. In particular if P increases, V decreases and vice versa. Around 1660 the
Irish scientist Robert Boyle found that the relationship between P and V for a gas when the temperature is constant is a branch of equilateral hyperbola.
The same relationship that Boyle identified can be determined more conveniently if we perform measurements of the volume as P varies at constant T.
Equation of State of Ideal Gases
The equation of state of ideal gases describes the behavior of an ideal gas.
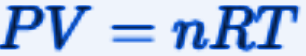
Where:
-P is the pressure of the gas,
-V is the volume of the gas,
-n is the number of moles of the gas,
-R is the universal gas constant,
-T is the absolute temperature of the gas.
Conclusions
The gaseous state represents one of the fundamental forms of matter and the elements that are in this state acquire unique properties.
Gases have been and still are useful for the development of technologies and industrial processes.
Question
Among the most well-known and used gases in the industrial field are oxygen (O2), nitrogen (N2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and argon (Ar). Did you know that argon is often used in triple-glazed windows to improve thermal insulation?

[ITALIAN]
20-03-2025 - Basi di chimica - Stato gassoso [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_75)
Stato gassoso

Immagine generata con IA, software usato Microsoft Copilot
Definizione
Gli stati fondamentali della materia sono 4:
-Solido
-Liquido
-Gassoso
-Plasma
Quindi lo stato gassoso è uno dei quattro stati fondamentali della materia, stato in cui le molecole di una sostanza sono separate da distanze molto grandi rispetto alle dimensioni delle molecole stesse. Questa condizione fa in modo che i gas si possono espandere per riempire il volume del contenitore in cui si trovano a di avere una densità molto bassa rispetto ai solidi e ai liquidi.
Caratteristiche
Qui di seguito sono elencate le caratteristiche principali attribuite allo stato gassoso.
-Espansione
-Compressibilità
-Bassa densità
-Miscibilità
dove:
Miscibilità = tendenza dei gas a mescolarsi completamente tra loro formando miscele omogenee.
Pressione
La pressione è una delle proprietà fondamentali che caratterizzano lo stato gassoso.
La pressione P è la forza che un corpo esercita su una superficie di area unitaria in direzione normale alla superficie stessa. Nel Sistema Internazionale (S.I.) la pressione si misura in Pascal (Pa) oppure in bar.
Per misurare la pressione sono comunque usate, in tutto il mondo, altre unità di misura.
-atmosfere (atm);
-millimetri di colonna di mercurio (mm Hg);
-torricelli (torr) in onore del fisico Evangelista Torricelli;
-metri di colonna d’acqua (m H2O);
-psi
Qui di seguito una riga in cui sono espresse le varie unità di misura e la relazione tra di esse.
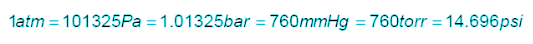
Legge di Boyle
Una delle leggi principali che coinvolgono la pressione e i gas è appunto la Legge di Boyle.
La legge di Boyle descrive la relazione tra la pressione (P) e il volume (V) di un gas a temperatura costante.
P x V = costante
Legge di Gay-Lussac
Un altra legge importante nello studio dello stato gassoso è quella di Legge di Gay-Lussac.
La legge di Gay-Lussac descrive la relazione tra la pressione (P) e la temperatura (T) di un gas a volume costante. Essa afferma che la pressione di un gas è direttamente proporzionale alla sua temperatura assoluta.
P / T = costante
Nota: P e T sono grandezze intensive: non dipendono dall’estensione del sistema ma solo dal punto in cui vengono valutate e dall’istante temporale.
Temperatura
Quando siamo nell'ambito dello studio dei gas possiamo dire che la temperatura è una delle variabili chiave che influenzano il comportamento dei gas.
Relazione tra gas e temperatura
Quando la temperatura di un gas aumenta, le molecole del gas acquisiscono più energia cinetica ed iniziano a muoversi più velocemente. Questa condizione crea una espansione del gas se il volume è variabile, oppure un'aumento della pressione se il volume è costante.
Nel S.I. si misura in kelvin (K), che è un’unità di misura assoluta, nel senso che 0 K è lo zero assoluto della temperatura: non è possibile scendere al di sotto di questo valore.
Legge di Charles
In questo caso possiamo citare La legge di Charles, la quale afferma che il volume di un gas è direttamente proporzionale alla sua temperatura assoluta a pressione costante. Quindi la relazione è la seguente
V / T = costante
Equazione di stato dei gas
Tramite un esperimento rudimentale con un pistone ed un contenitore possiamo osservare quanto segue.
Assegnata T e facendo variare P si osserva che il volume V varia. In particolare se P aumenta, V diminuisce e viceversa. Intorno al 1660 lo
scienziato irlandese Robert Boyle trovò che la relazione tra P e V per un gas quando la temperatura è costante è un ramo di iperbole equilatera.
La stessa relazione che individuò Boyle può essere determinata in maniera più conveniente se si eseguono misure del volume al variare di P a T costante.
Equazione di Stato dei Gas Ideali
L'equazione di stato dei gas ideali descrive il comportamento di un gas ideale.
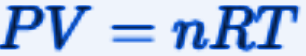
Dove:
-P è la pressione del gas,
-V è il volume del gas,
-n è il numero di moli del gas,
-R è la costante universale dei gas,
-T è la temperatura assoluta del gas.
Conclusioni
Lo stato gassoso rappresenta una delle forme fondamentali della materia e gli elementi che si trovano in questo stato acquisiscono proprietà uniche.
I gas sono stati e sono tuttora utili per lo sviluppo di tecnologie e processi industriali.
Domanda
Tra i gas più conosciuti ed usati nel campo industriale sono l'ossigeno (O2), Azoto (N2), Anidride carbonica (CO2) e l'Argon (Ar). Lo sapevate che l'argon è spesso utilizzato nelle finestre a triplo vetro per migliorare l'isolamento termico?
THE END
I Always love how you always explain your stuff in a very simpler form every single time
Thanks for stopping by. From a chemical point of view, the gaseous state is characterized by a set of particles (i.e. atoms or molecules) that move rapidly and randomly. The key properties of gases are: chaotic motion, low density and high compressibility, expansion, pressure, diffusion. !hiqvote
@stefano.massari, the HiQ Smart Bot has recognized your request (1/2) and will start the voting trail.
In addition, @consistency gets !PIZZA from @hiq.redaktion.
For further questions, check out https://hiq-hive.com or join our Discord. And don't forget to vote HiQs fucking Witness! 😻
Thanks for ecency curation! Ecency is definitely the HIVE front end application that I use the most for reading posts and making comments.
Do you have any idea why the number of modules is usually written n and not N?
Thank you for asking this question. In the formula 𝑃𝑉=𝑛𝑅𝑇, n represents the number of moles. This is a universally accepted convention in chemistry and physics in the context of the ideal gas formula. !DIY
You can query your personal balance by
!DIYSTATS@stefano.massari, you're rewarding 1 replies from this discussion thread.