18-03-2025 - Chemistry Basics - Crystal Structure [EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
18-03-2025 - Chemistry Basics - Crystal Structure [EN]-[IT]
With this post I would like to give a brief instruction on the topic mentioned in the subject
(code notes: X_77)
Crystal Structure
Definition
When we talk about the crystal structure of a material we are verifying the spatial ordering of the atoms, or ions or molecules that compose it.
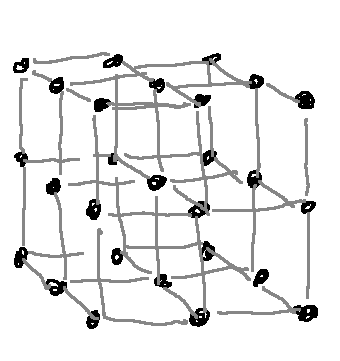
Below is a sketch of a simple cubic lattice crystal structure
Crystalline solids
Crystalline solids are those in which the atoms, ions or molecules that make up the material are arranged three-dimensionally with a regular structure that shows an ordering with distances greater than the atomic dimensions. These distances are also called long-range distances.
An example is quartz (SiO2)
Amorphous Solids
In amorphous solids the particles are arranged in a disordered manner, so it is the exact opposite of crystalline solids.
An example can be glass (SiO2), here too the main chemical composition is the one seen for quartz

Fundamental characteristics of the crystalline structure
Below are listed some fundamental characteristics of the crystalline structure.
-Unit cell
-Crystal lattice
-Atomic sites
-Symmetry
-Packing density
Types of crystal structures
Here are the 5 types of crystal structures:
-Simple cubic structure (SC)
-Body-centered cubic structure (BCC)
-Face-centered cubic structure (FCC)
-Hexagonal close packed structure (HCP)
-Complex structures (an example are those of silicates):
Effects on materials
The regular arrangement of atoms influences various properties of materials. Here is a list of the most important ones:
-Mechanical properties
-Thermal properties
-Electrical properties
-Optical properties
Some notes about the crystalline structure of some materials
sodium chloride
Sodium chloride (NaCl) has a well-defined crystalline structure. Sodium chloride crystallizes in a lattice called "rock salt" which is inserted in the face-centered cubic (FCC) typology for chloride ions.
In Sodium Chloride the bond is mainly due to electrostatic forces
a molecular solid
In a molecular solid the fundamental units are the molecules and the crystalline structure describes how these molecules are arranged. We can say that they identify what is the ordered lattice with respect to the space of the fundamental units.
When a molecular solid is melted, the absorbed energy serves to overcome the forces of attraction between the molecules.
Conclusions
The crystalline structure is the regular ordering of the atoms of a solid and this is important for understanding the physical properties of that particular material.
Question
Do you remember ever having seen crystalline structures of some material?

[ITALIAN]
18-03-2025 - Basi di chimica - Struttura cristallina [EN]-[IT]
Con questo post vorrei dare una breve istruzione a riguardo dell’argomento citato in oggetto
(code notes: X_77)
Struttura cristallina
Definizione
Quando parliamo della struttura cristallina di un materiale stiamo verificando l'ordinamento spaziale degli atomi, o degli ioni o delle molecole che lo compongono.
Qui di seguito riporto uno schizzo di una struttura cristallina di tipo reticolo cubico semplice

Solidi cristallini
I solidi cristallini sono quelli per cui gli atomi, gli ioni o le molecole che costituiscono il materiale, sono disposti tridimensionalmente con una struttura regolare che mostra un ordinamento con distanze maggiori delle dimensioni atomiche. Queste distanze vengono chiamate anche distanze a lungo raggio.
Un esempio può essere il quarzo (SiO2)

Solidi Amorfi
Nel solidi amorfi le particelle sono disposte in maniera disordinata, quindi è l'esatto contrario dei solidi cristallini.
Un esempio può essere il vetro (SiO2), anche qui la composizione chimica principale è quella vista per il quarzo

Caratteristiche fondamentali della struttura cristallina
Qui di seguito sono elencate alcune caratteristiche fondamentali della struttura cristallina.
-Cella elementare
-Reticolo cristallino
-Siti atomici
-Simmetria
-Densità di impacchettamento
Tipi di strutture cristalline
Qui di seguito le 5 tipologie di strutture cristalline:
-Struttura cubica semplice (SC)
-Struttura a corpo centrato (BCC)
-Struttura cubica a facce centrate (FCC)
-Struttura esagonale compatta (HCP)
-Strutture complesse (un esempio quelle dei silicati):
Effetti sui materiali
La disposizione regolare degli atomi influenza diverse proprietà dei materiali. Qui di seguito un elenco delle più importanti:
-Proprietà meccaniche
-Proprietà termiche
-Proprietà elettriche
-Proprietà ottiche
Alcune note a riguardo della struttura cristallina di alcuni materiali
cloruro di sodio
Il cloruro di sodio (NaCl) possiede una struttura cristallina ben definita. Il cloruro di sodio cristallizza in un reticolo definito "salgemma" che viene inserito nella tipologia cubico a facce centrate (FCC) per gli ioni cloruro.
Nel Cloruro di sodio il legame è dovuto principalmente a forze elettrostatiche
un solido molecolare
In un solido molecolare le unità fondamentali sono le molecole e la struttura cristallina descrive come queste molecole sono disposte. Possiamo dire che identificano quel è il reticolo ordinato rispetto allo spazio delle unità fondamentali.
Quando si fa fondere un solido molecolare, l’energia assorbita serve a vincere le forze di attrazione tra le molecole.
Conclusioni
La struttura cristallina è l'ordinamento regolare degli atomi di un solido e questa è importante per comprendere le proprietà fisiche di quel determinato materiale.
Domanda
Ricordate di aver mai visto delle strutture cristalline di qualche materiale?
THE END
The crystal structure really defines so many properties of materials!
Have you ever seen salt crystals up close?
They naturally form perfect cubic shapes! 💎
Thanks for stopping by! I have never seen salt crystals up close. From what you wrote I assume they have a perfect cubic alignment. From what I know it should have a face centered cubic structure.
I haven’t seen this kind of material before
The only one I’m familiar with is a material that looks like a dog cage…
Hi bisolamih Salt crystals, especially sodium chloride (NaCl), have a cubic shape. They might actually look like a cage.
The chemistry is amazing how to convert the water in wine for example, unfortunately I am not good student In this.
I remember been taught about this particular topic in school which I didn't really understand
actually it is not an easy topic. Perhaps the simplest thing is the formation of salt crystals. However I must admit that when we talk about crystals in chemistry the shapes are different and they also have a name frame not easy to remember.
@stefano.massari, you're rewarding 4 replies from this discussion thread.