06-07-2024 - Energy systems - The reaction turbine[EN]-[IT]
~~~ La versione in italiano inizia subito dopo la versione in inglese ~~~
ENGLISH
06-07-2024 - Energy systems - The reaction turbine[EN]-[IT]
The reaction turbine
Parsons Turbine
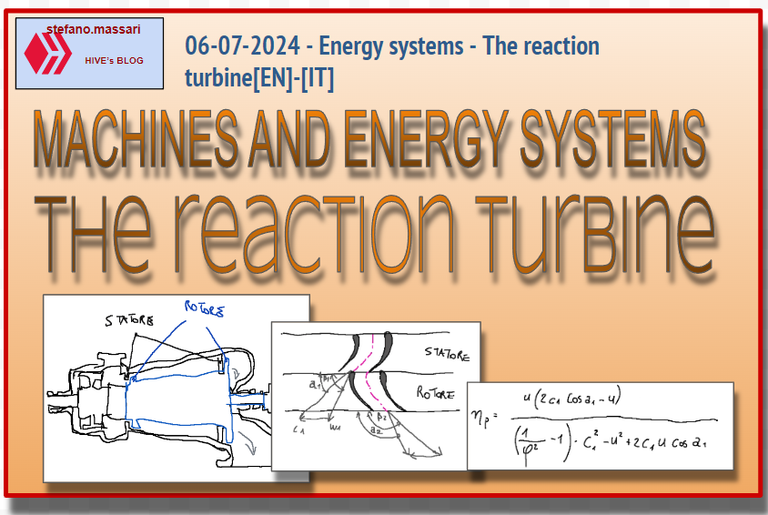
Parsons type steam turbines are reaction turbines, almost always multiple and with a drum structure.
Operation
The operating phases of a Parsons turbine are described below.
-high pressure steam enters the turbine through a series of fixed nozzles.
-The steam enters the various stages. This turbine is composed of many successive stages, each of which contains fixed blades (stator) and movable blades (rotor).
-The gradual conversion of energy occurs as the Parsons turbine uses the reaction configuration, in which the steam undergoes a pressure drop in both the fixed and mobile blades.
-rotation of the rotor
-steam exhaust
NOTE 1:
The Parsons turbine has pressure differences between the upstream and downstream of each individual stage
NOTE 2:
Parsons turbines are often preceded by one or more acting stages.
In fact, in the most common installations, these turbines are preceded by one or more action stages. These stages have the function of processing a large part of the total enthalpy change available.
NOTE 3:
Compared to a De Laval turbine, the stage of a Parsons turbine is capable of higher efficiency and operates in conditions of maximum efficiency with a lower u/c1 ratio.
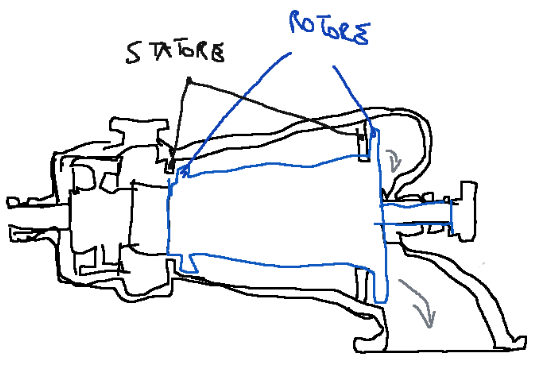
Speed triangles
Below is a sketch regarding the speed triangles of a multi-stage reaction axial turbine.
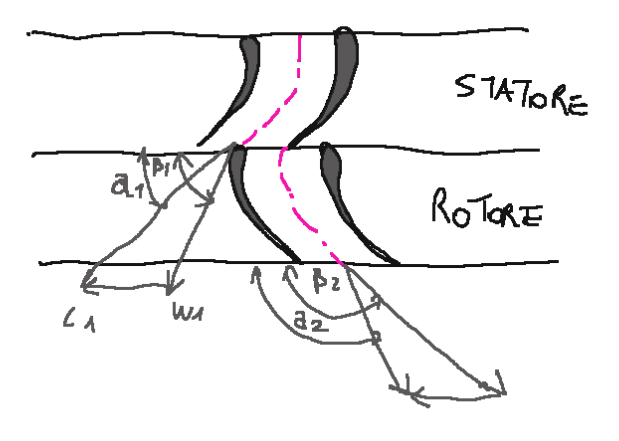
Yield
The blading efficiency of a Parsons turbine is defined as follows.
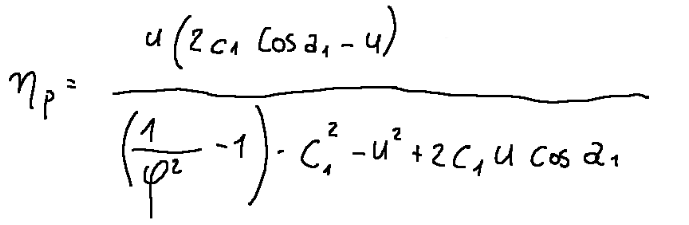
The maximum blading efficiency value of a Parsons turbine is 0.8
Conclusions
The Parsons turbine represents a major development in steam turbine engineering. This particular turbine was introduced by Sir Charles Parsons in 1884. A high efficiency turbine.
Request
Have you ever heard of the inventor Charles Parsons before?

ITALIAN
06-07-2024 - Sistemi energetici - La turbina a reazione[EN]-[IT]
La turbina a reazione
Turbina Parsons
Le turbine a vapore tipo Parsons sono turbine a reazione, quasi sempre multiple e con struttura a tamburo.

Funzionamento
Qui di seguito sono descritte le fasi di funzionamento di una turbina Parsons.
-il vapore ad alta pressione entra nella turbina attraverso una serie di ugelli fissi.
-Il vapore entra nei vari stadi. Questa turbina è composta da molti stadi successivi, ognuno dei quali contiene palettature fisse (statore) e palettature mobili (rotore).
-Avviene la conversione graduale dell’energia in quanto la turbina Parsons utilizza la configurazione a reazione, in cui il vapore subisce una caduta di pressione sia nei palettamenti fissi che in quelli mobili.
-rotazione del rotore
-scarico del vapore
NOTA 1:
La turbina Parsons presenta differenze di pressione tra monte e valle di ogni singolo stadio
NOTA 2:
Le turbine Parsons sono spesso precedute da uno o più stadi ad azione.
Infatti, ,nelle installazioni più comuni, queste turbine sono precedute da uno o più stadi ad azione. Questi stadi hanno la funzione di elaborare gran parte del salto entalpico totale disponibile.
NOTA 3:
Rispetto ad una turbina De Laval, lo stadio di una turbina Parsons è capace di rendimenti superiori ed opera in condizioni di massimo rendimento con un rapporto u/c1 inferiore.
I triangoli delle velocità
Qui di seguito uno schizzo che riguarda i triangoli delle velocità di una turbina assiale a reazione pluristadio.

Rendimento
Il rendimento della palettatura di una turbina Parsons si definisce come segue.
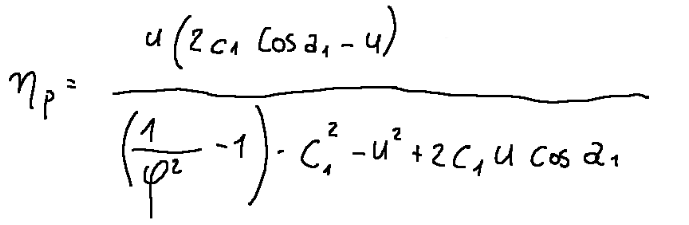
Il valore massimo di rendimento della palettatura di una turbina Parsons è di 0,8
Conclusioni
La turbina Parsons rappresenta un importante sviluppo nell'ingegneria delle turbine a vapore. Questa particolare turbina fu introdotta da Sir Charles Parsons nel 1884. Una turbina ad alta efficienza.
Domanda
Avete mai sentito nominare prima d'ora l'inventore Charles Parsons?
THE END
The efficiency of Parsons turbine is explanatory but quite difficult
Thanks for the topic though
I loved it
This is quite hard though😁😁😁
The Parsons turbine's efficiency is pretty cool, though it's complex to grasp fully. Thanks for the detailed explanation brother, nice work