The life cycle of flowering plants part I
(Edited)
The studying of morphology, the life stages and the functions of flowering plants is very paramount for us to know how plants behave and how we can better understand their development and better depend on them as secondly and tertiary consumers. Plants being "Producers"have ability to manufacture their own food through photosynthesis by combining water, CO2, energy from the sun to produce glucose and leaving O2 in the atmosphere for respiration 🫁 for other living organisms. Such mechanism is great natural phenomenon that plants possess and different from we the consumers. We as humans are in the position to support and encourage their better growth without any hindrance.
For every cycle as we know is a process of stages that something goes through in a circular motion,ends and continue the process again. To me, the life cycle of flowering plant begins from the parent plant which gives rise to their young ones; that's seeds. The seeds will germinate to form seedlings or young plants. The seedlings would reach maturation stage. It would reach to a point where the matured plants bear flowers. When it bears flowers, pollination has to take place followed by fertilization. After fertilization,the fruit would form and seeding would be produced. When the fruits and seeds mature, it would dispersed and the cycle continue again.
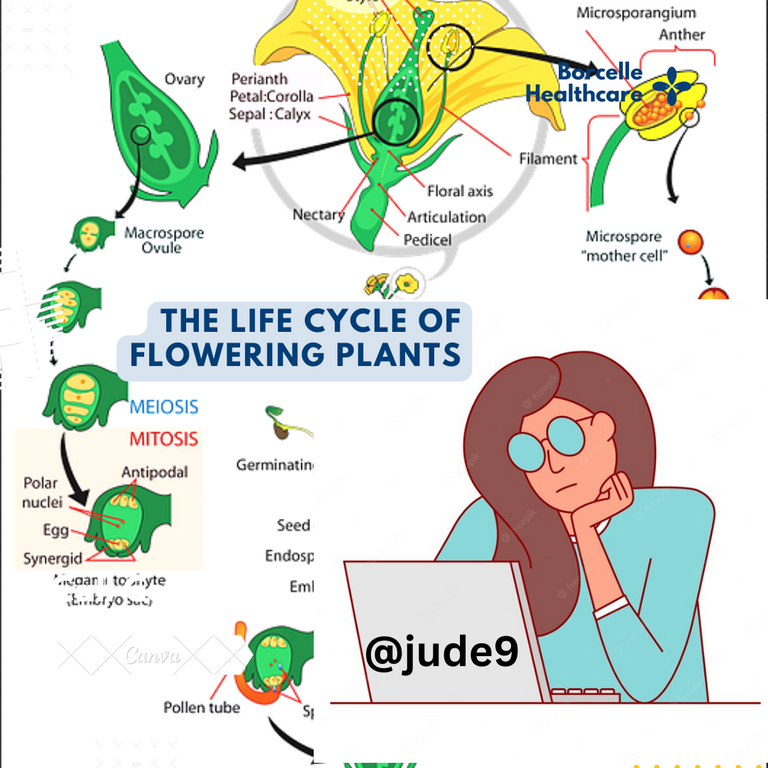
The Structure of a Flower
The components or parts that form a flower is very complex thing with many functions. Each component is very vital to the whole plant,some of them function as a group. It begins from the "stalk." The stalk is the long branch which extends from the stem to the flower. It function is to hold the flower firmly in position. It's the part which support the transport of food nutrients, H2O, and O2 to the flower. The next to the stalk is the "sepals" which are located at the base of the flower. Sepals are very green in nature and they portray a great photosynthetic pigment. Their number would differ from flower to flower. They protect the flower at its bud stage. In many flowers they appear as 4. A group of sepals are called calyx. Just after the calyx are the petals which are brightly coloured part of the flower. They come with different colours depending on the kind of the flower. A group of petals are called Corolla. They attract insects like bees for pollination due to their brightly colour nature. They also have good scent that attract insects to the flower.
The filament is the long thin part of a flower inside the petals. They hold firmly the anther which is the male part of the flower. Without the filament, the anther can't be hanged on the flower. The "Anther" is the part that contains the pollen grain that's a powdery substances which is the male sex cell for pollination. The filament and anther surround the carpel consisting of the stigma, the style and ovary. The stigma is the female reproductive organ that receives the pollen grains for fertilization during pollination. There is a pollen tube which is a hole through the style. This tubes help the passage of the pollen grains during fertilization. The ovary produces fruits while the ovule produces seeds which are found in the fruits. The difference between the ovary and the ovule of flowering plants is simple. The ovary mostly have 2 scars while the ovules have 1 scar. The epicarp of ovary is very soft while in the ovule is very hard.
Fruits/seeds maturation and dispersal
Following fertilization of fruits and seeds formation, they mature. As we have discussed, the ovary grows into fruits and ovules into seeds. In most cases flowering plants found in bushes have their fruits and seeds dispersed to further the cycle. Dispersal of fruits or seeds are the process whereby the fruits and seeds are transferred from their parent plants to other places to continue their life cycle. There are actually many agents for fruits and seeds dispersal. Some of these agents are water water, wind and explosive mechanisms. Fruits or seeds that would be dispersed by wind should be lighter and hairly to be able to carry by wind easily. Fruits and seeds that would be dispersed by water must have hollow like coconut. The explosive mechanisms are by natural means like bursting when there is excess drought or dry. There are really many things that goes on in the life cycle of flowering plants and we will continue in our next studies.
0
0
0.000
Thanks for your contribution. What are your sources?
Oh, sorry I'll put it now. I just forgot when I finished.
I've now done it. Thanks 🙏
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.