Metabolism - An Overview of Energy Production and Nutrition
Hello everyone, I was really happy seeing the level of engagement on my previous post, thanks a lot to everyone who took the time to read the post. I also had fun reading some very interesting posts, and some posts looked complex to the eyes but the brain could assimilate them in the end. Today, I will be explaining metabolism and its importance in maintaining the body's functions. I will be starting with putting food in the mouth. Some food contains macronutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins, and triglycerides. Let me do a quick explanation of these things;

Carbohydrate is basically made up of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms. It includes sugars, starches, and cellulose, and is an important source of energy for the body while playing important roles in metabolism. Carbohydrates can be subdivided into two main categories which are simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates. The Simple Carbohydrate which is also known as Simple sugar is composed of monosaccharides which are single sugar and disaccharides which are double sugar. To understand better, examples of simple sugars are glucose, fructose, and lactose. Complex carbohydrates on the other hand are known as polysaccharides and are made up of three or more sugar. Examples of complex sugars are starches and cellulose.
Protein is basically made up of Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and Nitrogen atoms. They are made up of chains of amino acids, which are linked together by peptide bonds. These amino acids are combined in different ways to form various forms of proteins, and there are about 20 different Amino acids that can combine together. Of the 20 amino acids, 9 are considered nutritionally essential in the body of adults. These 9 amino acids are leucine, methionine, isoleucine, tryptophan, histidine, lysine, threonine, valine, and phenylalanine.
Triglycerides are made up of Carbons, Oxygens, and Hydrogens, just like carbohydrates but the amount of Carbon and Hydrogen exceeds the Oxygen. Triglycerides are made of three fatty acids attached to a molecule of glycerol. Similar to carbohydrates, they are important sources of energy for the body and can be broken down into fatty acids and released into the bloodstream when needed, while the excessive amount is stored in the adipose tissues of the body. Excessive triglycerides in the blood are known as hypertriglyceridemia, and they can be dangerous to health.
When food is in the Gastrointestinal tract, starting with the mouth. In the mouth, saliva plays an important role in digesting carbohydrates. Saliva is made up of an enzyme called salivary amylase, and this is what is used to break down carbohydrates into glucose. For protein, once it gets to the stomach, Hydrochloric acid (HCL) which is the acid in the stomach creates an acidic environment and breaks the protein, after which Pepsin which is a protease molecular enzyme breaks down the protein into peptides and amino acids. In the Jujenum of the Small intestine, bile breaks down triglyceride, as well as lipase which breaks down fat, breaks down triglyceride to glycerol and fatty acid.
From the stomach, the glucose moves into the small intestine where it is absorbed into the bloodstream. Other simple sugars are Fructose, and Galactose. They are absorbed into the bloodstream through the wall of the small intestine where they are used for energy purposes, also they move to the liver where they are stored as glycogen. Also, Amino acid from the small intestine is absorbed into the bloodstream where it is used for various functions in the body, and then towards the liver. While both Carbohydrate and Protein end products go to the bloodstream, triglyceride is completely different. It doesn't go into the bloodstream leading to the liver. The amino-acid and Glycerol are absorbed into the lymphatic system, where it is distributed into different tissues of the body, then to the liver.
Glucose in the liver can be stored in form of Glycogen (inactive and stored form of glucose), in a process known as Glycogenesis.
With the involvement of several chemical reactions, beginning with the activation of glucose into glucose-6-phosphate through the enzyme hexokinase. The Glucose-6-phosphate is converted to glucose-1-phosphate and then converted into UDP-glucose which is then synthesized into glycogen. When the body's needs more energy when it lacks, the liver and muscles breaks down the glycogen into glucose and uses it for energy, in a process known as glycogenolysis. The breaking down of the glycogen to glucose is done through a chemical reaction by an enzyme known as glycogen phophorylase to release glucose-1-phosphate. The glucose-1-phosphate is then converted to Glucose through the enzyme glucose-1-phosphatase. The process of Glycogenolysis is regulated via insulin in other to maintain blood sugar level.
Wikimedia
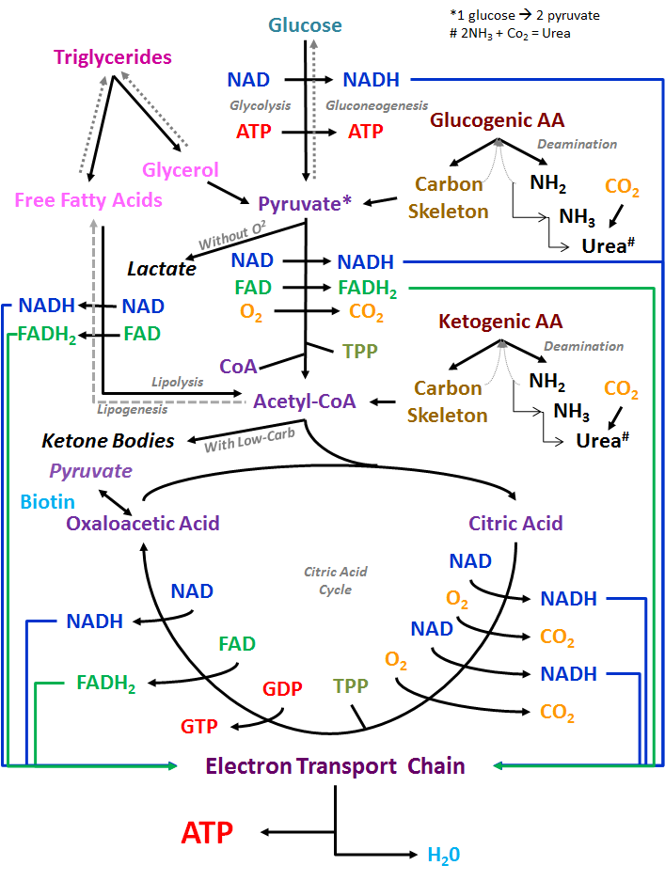
The Glucose in th liver could also be converted to pyruvate. which is a three-carbon compound which serves as an intermediate in the process of cellular respiration where glucose is used to produce energy, in a process called Glycolysis. Glycolysis begins with the breaking down of glucose into two molecules of three-carbon compound called glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate, which is then converted into two molecules of pyruvate. Pyruvate with go into the Mithochondrium to become Acetyl-CoA.
Acetyl-CoA play a major role in several metabolic pathways including citric acid cycle (Kreb Cycle), synthesis of fatty acids, and cholesterol. While pyruvate becomes Acetyl-CoA through the process of Glycolysis, Acetyl-CoA is formed from the breakdown of fatty-acids in the mitochondria through the process known as Beta-Oxidation. Acetyl-CoA with the combination of Oxaloacetate in the mitochondria will form the Kreb cycle. With Kreb Cycle , nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH) and flavin adenine dinucleotide (FADH) are produced.
NADH is produced when glucose, amino acid, and fatty acid is broken down, thereby transferring electron to produce ATP. NADH is produced in the Cytosol of the mitochondria through glycolysis, and in the mitochondria through kreb cycle. Similar to NADH, FADH is produced when glucose, fatty acids, amino-acids are broken down. It involves the transfer of electrons to produce ATP. It produces energy in the mitochondria through Kreb Cycle from the breakdown of Acetyl-CoA. To perform this, Oxygen is needed (Aerobic Respiration).
In cases where the oxygen isn't enough (Anaerobic respiration), lactate is produces from the pyruvate. Lactate is produced by cells when the demand for energy exceed the amount of oxygen being supplied. It can be converted back to pyruvate through the process called lactate oxidation.
Amino Acids when not used is not stored, it is converted to Urea and removed from the body. There are 20 different types of Amino Acids which are found in protein. They can be divided into Essential, non-essential, and Conditional amino acids, depending on how the body synthesizes them. The essential amino acids are leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, istidine, isoleucine, and valine. Non-essential amino acids are; alanine, asparagine, aspartic acid, glycine, proline, serine, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, tyrosine, and arginine. The conditional amino acids are arginine, and histidine. Some of the amino-acids function with Glycolysis, and some function with Kreb Cycle to produce ATP. Also, Fatty Acids, function with Kreb Cycle to produce ATP. When there is no glucose, Acetyl-CoA produces Ketones through Ketogenesis, which goes into the bloodstream, then to the liver then to the Brain to produce Acetyl-CoA through Ketolysis which is then returned to the Kreb Cycle.
Conclusion
In the body, a set of chemical reactions occur to maintain the state of life. This reactions have to do with breaking down nutrients, to produce energy as well as synthesising molecules necessary for the functionality of body tissues and organs. In other for us to do our activities and live, the body needs to perform some metabolic process.
Reference
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/carbohydrate
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/engineering/triglycerides
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/protein-metabolism
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/biochemistry-genetics-and-molecular-biology/acetyl-coa
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/glycolysis
You have received a 1UP from @gwajnberg!
@stem-curator, @neoxag-curator, @pal-curator
And they will bring !PIZZA 🍕.
Learn more about our delegation service to earn daily rewards. Join the Cartel on Discord.
Nice explanation
!1UP
Congratulations @elity-sitio! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain And have been rewarded with New badge(s)
Your next target is to reach 4750 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPCheck out our last posts:
Support the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!
I gifted $PIZZA slices here:
@curation-cartel(13/20) tipped @elity-sitio (x1)
Send $PIZZA tips in Discord via tip.cc!
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
Thanks for including @stemsocial as a beneficiary, which gives you stronger support.