Let's discuss why cross matching of blood cannot be done on neonates
Experience
I genuinely love babies but here I feel I was taken unexpectedly to receive my cousin's child. My favorite cousin was pleading that I come stay with her for a while since my school are on break, I took it in as a very good idea atleast to explore.
Yes, I love exploring, I travelled to her state in the country with the notion of just staying for a little while, atleast three weeks and I go back home. Little did I know that my cousin is about to put to birth or should I say she didn't know it will come so fast or earlier before the baby's estimated due date.
I knew absolutely nothing then, just knew my cousin was having some contractions, getting so weak and screaming it's not the due date yet. I never understood what she meant, I was thrown off balance.
To cut the whole story short,my cousin gave birth to a premature through cesarean operation due to the baby has low weight and hyperbilirubinemia so therefore, blood transfusion needed, carrying out the cross-matching test with the mom's blood.
My question then was, why is the mom (my cousin) going for a cross match test instead of the baby who needs the blood transfusion?
Greetings my lovely distinguished people of this community,I feel so thrilled for this very first time to share a knowledge I have come across, and learnt so far. I'm so delighted to be here.
Back to our discussion, Neonate is a baby of first 4weeks after birth, but when the baby is more than one month, they are no longer taken as neonate, it's also called Newborn.
These periods, they are very susceptible to severe infections because their antibodies are under developed, so as their organs too, A new born undergoing blood transfusion is sadden.
Based on a layman's understanding of blood transfusion is the transfer of blood from someone to the person in need of blood But in a medical definition - blood transfusion is the medical routine whereby donated blood from the donors are given to the recipients in a lying state through intravenous line, the blood transfusion is done to give or replace whole blood and blood components that may be too low in the recipient's body.
Plasma, platelets, cryoprecipitate, white cells and red cells are components of blood which makes up the transfused whole blood while the blood moves into the disposable biomedical transparent flexible poly vinyl chloride (PVC) container used for the collection, processing and storage of whole blood and blood components, which is called the BLOOD BAGS, while mixing the blood and anticoagulants in the bags every 45 seconds till it reaches the bag capacity, these blood bags are stored in a refrigerator for 42days @6°c, always available in 350 & 450 ml.
The anticoagulants which are inserted in the blood bags to avoid the blood from clotting as quickly as normal, thereby inhibiting the clotting factors of blood from coagulating, the most common anticoagulant in the blood bags is CPDA: Citrate Phosphate Dextrose Adenine - their unique functions are;
💫CITRATE– acts as anticoagulant by chelating calcium in the blood.
💫DEXTROSE- helps in the breakdown or metabolism of stored red blood cells.
💫PHOSPHATE- aids to lower the acidity and have a very highest concentration of 2,3 DPG and red cell phosphate
💫ADENINE- aids to keep the red blood cells viable.
A particular blood bag which has been stored is identified with a particular blood group written on it's body to avoid complications from occuring such as blood mismatch causing incompatibility and preventing lack of laboratory proficiency status.
For instance when a donated blood bag is not labelled A+ but was hurriedly and mistakenly given to a B+ person, this can cause blood group incompatibility. The resultant effect is destruction of the red blood cells of the recipients.
BLOOD GROUP
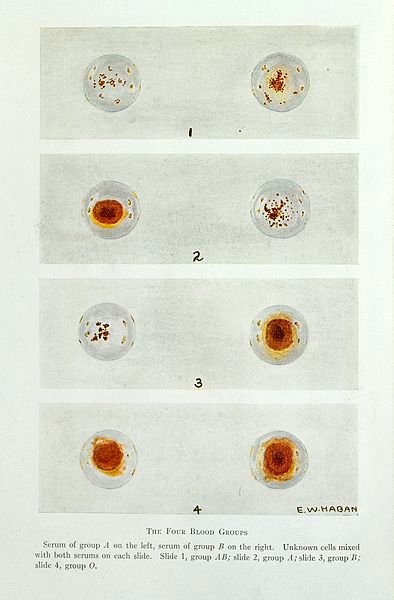
Everyone is identified with a particular blood group, also can be called Blood type -> Thou there are so many classifications of blood type but the most common blood group we know are blood group A, B, AB, O
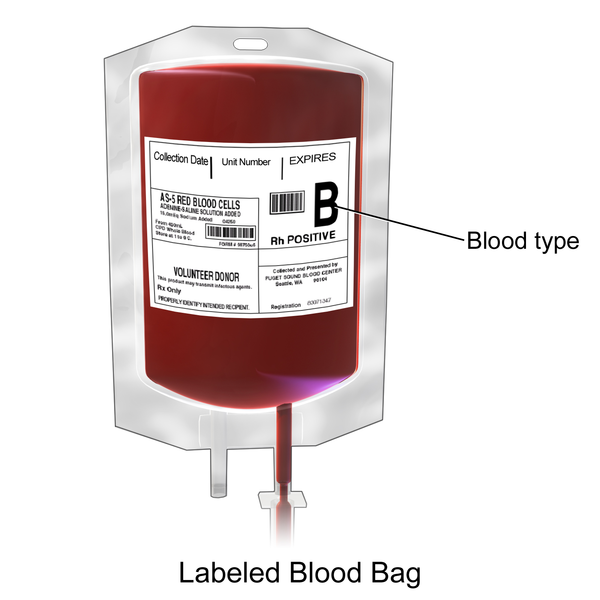
B positive 450ml blood bag for donation
These are the classifications of blood which has both presence and absence of antibodies and antigens that are inherited from parents. They are mainly found on the surface of the red blood cells, mostly, the Antigens.
Antibodies are proteins that are found in the blood plasma or serum of humans in response to antigens. What they do is to detect any invading foreign agent such as viruses etc and subsequently notifies the body's immune system, the resultant effect is their destruction. It also serve as a natural defender of the body,they are also called Antitoxins.
While Antigens serve as immune stimulating response, which are also protein molecules found on the surface of red blood cells. That is why it's said scientifically that washing of donor's blood cell with normal saline or mixing a buffer solution with whole blood- exposes the antigenic sites of the blood for the results of the test to take place.
Blood group A, B, AB, O represent a specific antibodies and antigens, that is;
💫Blood group A – carries A antigens on the red blood cells with Anti-B antibodies in the plasma
💫Blood group B – carries B antigens with Anti-A antibodies in the plasma.
💫Blood group O – carries no antigens , but * has both anti-A and anti-B antibodies* in the plasma
💫Blood group AB –carries has both A and B antigens , but no antibodies.
Precisely, Blood group O is the most common blood group, almost half of the population in the world has blood group O. The reaction that takes place between red cells and corresponding antibodies is called Agglutinations .
Note that, O RhD negative blood (O-) can safely be given to anyone without any issue. It's often used in medical emergencies when the blood type of the victim is not known. Rather than taking a risk with blood group O positive, O negative is given instead.
NB; Antigens on the surfaces of these red cells are noted as Agglutinogens and One can donate blood if you are healthy and fit, weighing about 50kg atleast, also people who are 17- 66 years old can donate blood atleast once in every 3months in a year if desired.
Red blood cells has another antigen, a protein known as the RhD antigen (Rhesus D antigen) , If this is present in your blood group, then your blood group is RhesusD positive If it's absent, so your blood group is RhesusD negative.
Roughly, medical statistics has recorded about 80% of people in the world are RhD positive while 20% do not have RhesusD antigen in their blood, meaning, they are Rhesus D negative (i.e RhD negative).
Whereas RhD antibodies originates after some medical organ transplant, transfusions, pregnancy exposing the individual to RhD antigens, these antibodies RhD (also known as anti-D) damage RhD positive red cells and cause haemolytic transfusion reactions.
Should the maternal antibodies from the mother cross the placenta and enter into the unborn child during pregnancy, it leads to haemolytic disease of the newborn ( the damage red blood cells).
Seemingly, individuals with RhD negative should not be transfused with RhD positive red cells, most especially RhD negative women of childbearing age but if there's an emergency where If transfusion of a RhD positive blood to RhD negative recipient is unpreventable, a haematologist should be consulted so as anti-D immunoglobulins to be administered immediately.
Therefore we have 8 blood groups, they are:
A RhD positive (A+)
A RhD negative (A-)
B RhD positive (B+)
B RhD negative (B-)
O RhD positive (O+)
O RhD negative (O-)
AB RhD positive (AB+)
AB RhD negative (AB)
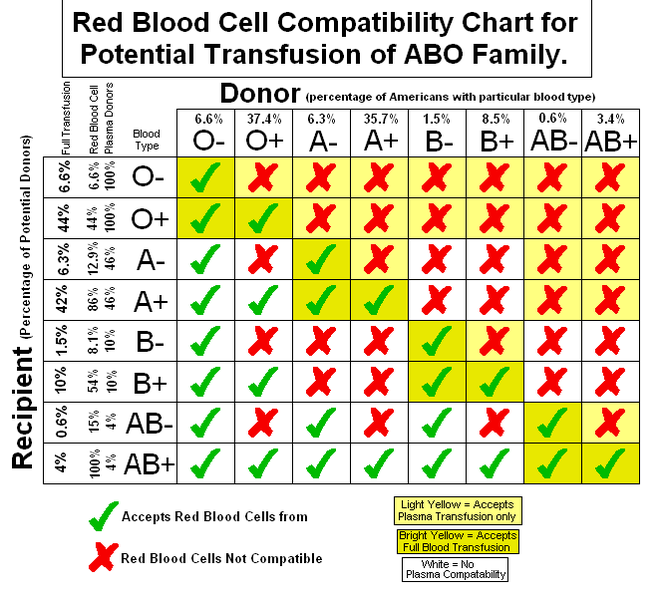
Blood compatibility panel test
All protocols been observed, a test carried out before the collection of blood group for blood transfusion is called CROSS MATCHING TEST.- The aim of this test is to the presence of antibodies in the recipients against the red blood cells of the donor,these antibodies gets attach to the red blood cells of the donor after transfusion.
This test is done before the transfusion of blood, any incompatible transfusion can result to death or even a severe hemolytic anemia.
How to cross match neonates
Appropriate selection of donors blood group is very necessary to avoid transfusion damage. Human ABO antigen are formed prebirth since they are genetically controlled by some genes. Corresponding antibodies are produced against them. Newborn babies do not produce ABO antibodies until they are up 3 to 6 months of age.
In cross-matching test, it can be done either Forward grouping (cell grouping) or Reverse grouping (serum grouping) - where in forward grouping tests the ABO antigens in Red blood cells, whereas reverse grouping tests the ABO antibodies in the serum.
Therefore, the ABO antibodies present in the serum of newborn babies are derived from mothers blood due to placental transfer and their bone marrow for the proliferation of cells is under developed.
The passive immunity passed on from the mother at birth also doesn't last and it begins to decrease in the first few weeks and months after birth. So cross-matching blood group of the newborn baby is done by ABO antigen grouping (forward grouping) only, and reverse grouping ur (ABO antibody grouping) is not needed.
In this case of transfusion of blood in newborn under 4 months of age, cross-matching of donors blood are performed with the mothers blood if available.
It's known that recipients of same group of blood is preferred in cases of transfusion in adults or older children But in the scenario of blood transfusion in infants under 4months of age and it's selection are dependant on the mothers blood group.
If the mothers blood group differs from the infant's blood group while the infant siblings are of the same group of blood,it will not be selected for transfusion. For instance, if the mother's blood group is blood group O and the newborn blood group is A, infants siblings of the same blood group A could not be transfused, because the anti-B antibodies can be derived in the infants serum from mothers blood which ll react with the A antigen of the donors blood.
In this case O group packed RBCs should be picked up for transfusion. Blood group O whole blood may contain IgG anti-A and anti-B antibodies in the plasma which can react with the A or B antigen of the infants blood. So to avoid anti-A & anti-B antibodies in O group, plasma should be discarded and the packed red blood cells should be transfused.
Because,antibodies of the anti-A & anti-B can be derived in the infants serum from mothers blood which may react with the A or B antigen of the donors blood. In this case blood group O packed red blood cell s should be chosen for transfusion.
Donor Blood group "O" whole blood may contain antibodies A and B in their plasma which can react with the infants blood either A or B antigen. So to prevent anti-A & anti-B antibodies in O group, Red blood cells should be transfused while plasma should be disposed completely.
In situation where there's Rhesus D-negative mother with Rhesus D positive baby, Rhesus D antibody may develop in mothers blood and it enters the baby's circulation. Here, the infant should be transfused with Rh-negative blood to prevent Rhesus D antigen & antibody reaction.
So in all clear indication that neonates under 4months has not developed their own antibodies due placental transfer of mother to child in that period,if sequential cases like this of neonatal transfusion it's taken with caution to avoid errors such as anemia etc.
I hope this was impactful and beneficent,really anticipate a good feedback from everyone here based on this topic.
Thanks.
My selected references
Selection of Blood (Packed RBCs) for Transfusion in Newborn Baby up to the Age of 4 Months
Sample requirements for Grouping and Crossmatching in Neonates
Blood Group Selection in Newborn Transfusion - Dr Padmesh - Neonatology
Exchange Transfusion: Neonatal - The Royal Children's Hospital
Congratulations @bloomcindy! You have completed the following achievement on the Hive blockchain and have been rewarded with new badge(s):
Your next target is to reach 300 upvotes.
You can view your badges on your board and compare yourself to others in the Ranking
If you no longer want to receive notifications, reply to this comment with the word
STOPSupport the HiveBuzz project. Vote for our proposal!
Every topic always has alot to be discussed. It didn't occur to me to discuss this in my previous write up on transfusion.
Well done.
Would like to read a more simplified version of this. It's kind of difficult to read, to be honest. I hope the user can improve her writing with time - under your guidance.
Thanks for your contribution to the STEMsocial community. Feel free to join us on discord to get to know the rest of us!
Please consider delegating to the @stemsocial account (85% of the curation rewards are returned).
You may also include @stemsocial as a beneficiary of the rewards of this post to get a stronger support.